Recently, under the leadership of Dong Yang and with core contributions from the research teams of Yixin Zhu, Hao Dong, and He Wang, the project titled "Research on Generalizable Dexterous Manipulation Technology for Embodied Intelligence Based on Cognitive Reasoning" underwent evaluation by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission and the Zhongguancun Management Committee, successfully passing the comprehensive performance assessment.
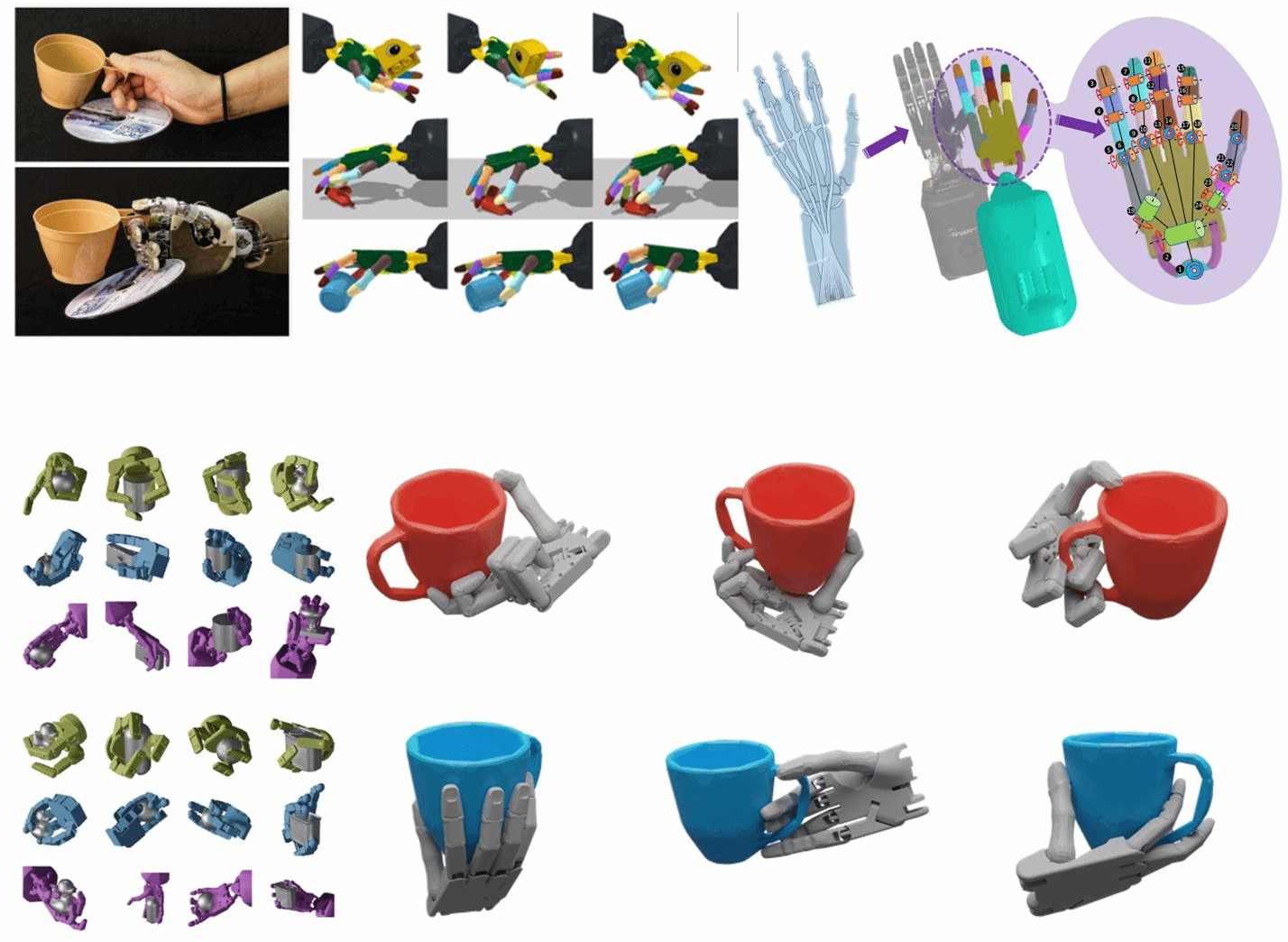
Figure 1. Diverse Dexterous Hand Manipulation Methods and Objects
In today's global context, robotic technology has gradually become a core component in various fields such as industrial automation, medical surgery, and home services, especially in the realm of dexterous manipulation. The essence of dexterous manipulation lies in endowing robots with decision-making capabilities to flexibly handle various objects, enhancing their generalized autonomous decision-making abilities and adaptability in complex scenarios, enabling them to respond to different environments and tasks much like human hands. However, achieving robotic dexterous manipulation still faces multiple technical challenges, such as handling objects of various shapes, including unseen ones, and achieving efficient motion planning based on precise environmental perception to adapt to changing scenarios.
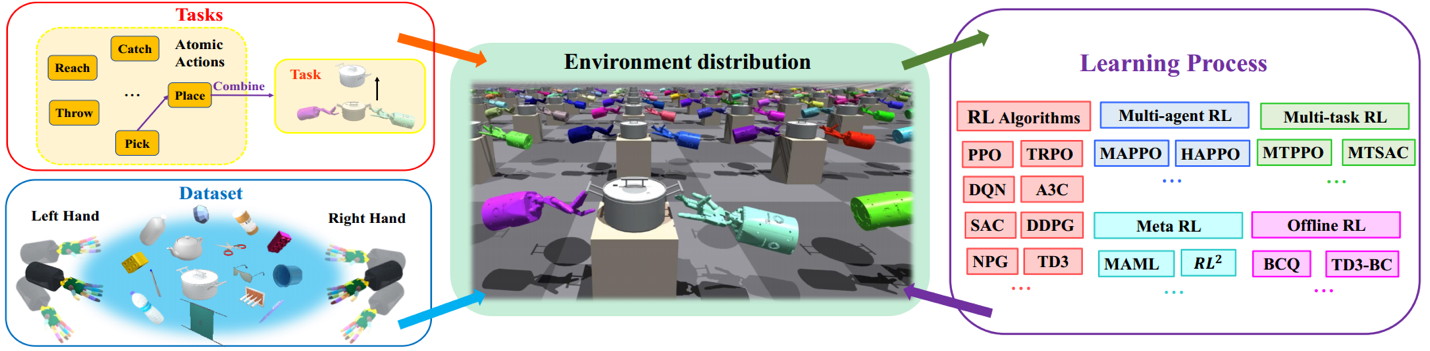
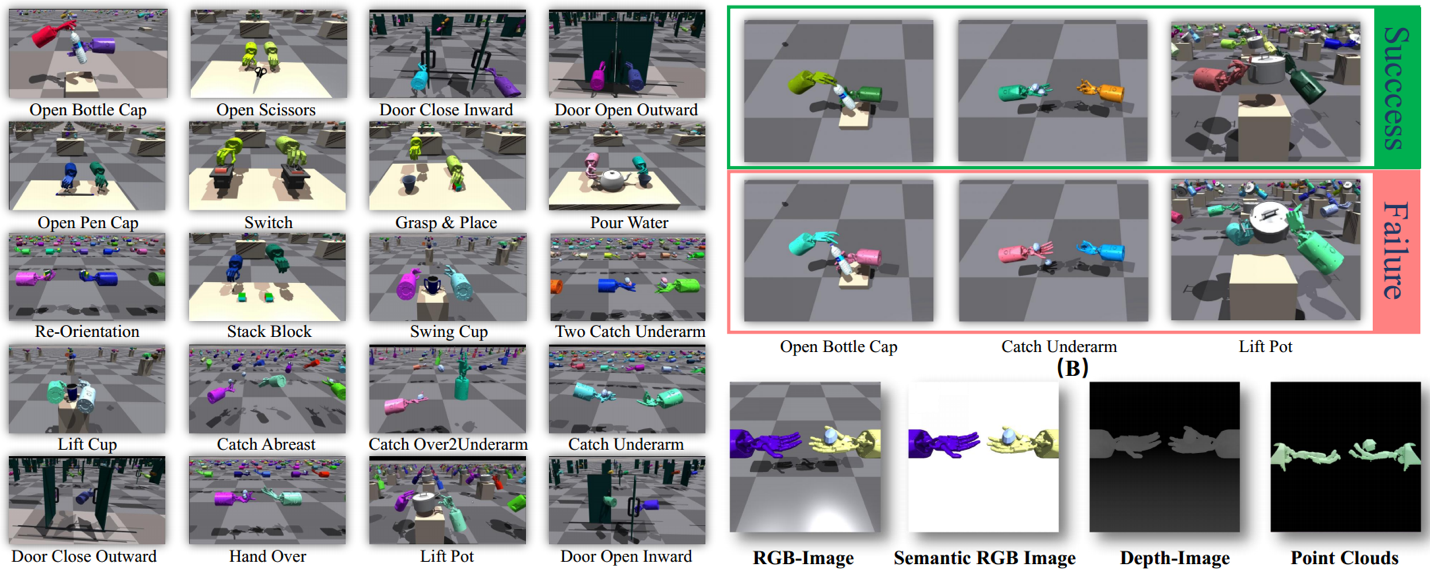
Figure 2. Overall Framework and Rich Task Types of the Bi-DexHands Simulation Platform
Leveraging cognitive reasoning, reinforcement learning, and computer vision technologies, the research team has focused on addressing core issues such as the limited generalization and safety of existing robotic hand grasping strategies since 2022, which often handle only single types of objects, and the lack of highly simulated platforms and datasets.
Specifictly, the team conducted research in system construction, data collection, task-specific grasping algorithms, and generalizable grasping operations. They successfully developed an efficient dexterous robotic hand simulation system suitable for single/multi-agent learning algorithm research, establishing it as a significant benchmark environment in the field of dexterous manipulation. Additionally, they constructed a high-quality, diverse, large-scale dexterous robotic hand grasping dataset. By employing cognitive reasoning techniques, they significantly enhanced the generalization capabilities of robotic hands across various target objects, complex hand configurations, diverse grasping postures, and tasks. They obtained general dexterous robotic hand grasping strategies and successfully deployed the proposed solutions in vision-based real-world complex robotic hand grasping tasks, achieving outstanding results.

Figure 3. Heterogeneous-Agent Reinforcement Learning Framework
Based on the technologies utilized in this project, Dong Yang's research team won the championship in the NeurIPS 2022 Dexterous Manipulation Challenge, ranking first among 340 teams. The related research has been published in 11 academic papers in top conferences and journals in computer science and robotics. Notably, the Bi-DexHands dual dexterous hand simulation platform developed by the team can run thousands of environments in parallel, achieving a simulation frame rate of over 65,000 frames per second on a single NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU, providing an efficient training system for dual dexterous hand learning. The design of dexterous manipulation tasks follows the principles of fine motor skills (FMS), establishing a mapping between infant ages and manipulation tasks. This provides a highly human-like robust benchmark for observing and evaluating the ability of robotic hands to manipulate objects and use tools at different developmental stages. Comprehensive benchmarks for single-agent/multi-agent/offline/multi-task/meta-reinforcement learning algorithms are provided for these tasks. The related paper, "Bi-DexHands: Towards Human-Level Bimanual Dexterous Manipulation," was accepted in November 2023 by the top international journal in the field of artificial intelligence, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), with an impact factor of 24.314. Furthermore, the team addressed the challenges of cooperation among heterogeneous dexterous hands by designing reinforcement learning algorithms suitable for heterogeneous multi-agent systems, providing theoretical guarantees for policy monotonic improvement and convergence. The related paper, "Heterogeneous-Agent Reinforcement Learning," was accepted in December 2023 by the top international journal in the field of machine learning, Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR). The team also achieved excellent results in international top academic conferences. One research work, "UniDexGrasp++: Improving Dexterous Grasping Policy Learning via Geometry-aware Curriculum and Iterative Generalist-Specialist Learning," received perfect reviews at ICCV 2023 and was nominated for the Best Paper Award. Another work, "GAPartNet: Cross-Category Domain-Generalizable Object Perception and Manipulation via Generalizable and Actionable Parts," received perfect reviews at CVPR 2023 and was selected as a Highlight, ranking in the top 2.5% of submitted papers. The open-source code repository related to the project has accumulated over 1,000 stars. Based on this research, the team has applied for two invention patents, aiming to apply the developed platforms and algorithms to intelligent prosthetic systems, providing technical support for safe and dexterous operations for individuals with disabilities. These research achievements have significantly enhanced China's academic status and industrial level in the field of dexterous manipulation, expanding the practical application scope of intelligent robots.


Figure 4. UniDexGrasp++ Learning Process and Performance Comparison


Figure 5. GAPartNet Framework and Object Manipulation Examples
In 2023, the field of embodied intelligent robots experienced rapid development. Simultaneously, the gradual improvement of relevant national policies and the strong support from science and technology departments such as the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission have further promoted technological innovation and commercial application of embodied intelligent robots. Among them, the dexterous manipulation module, as a core component of embodied intelligent agents, is one of the keys to promoting the application of robotic technology in real-world scenarios. In this context, the successful development and application validation of the project "Research on Generalizable Dexterous Manipulation Technology for Embodied Intelligence Based on Cognitive Reasoning" is particularly important and timely, once again demonstrating China's foresight and decision-making power in technological innovation and development.
This research work was supported by the "2022 Central Guidance for Local Science and Technology Development Special Project" of the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission's Beijing Science and Technology Plan.


